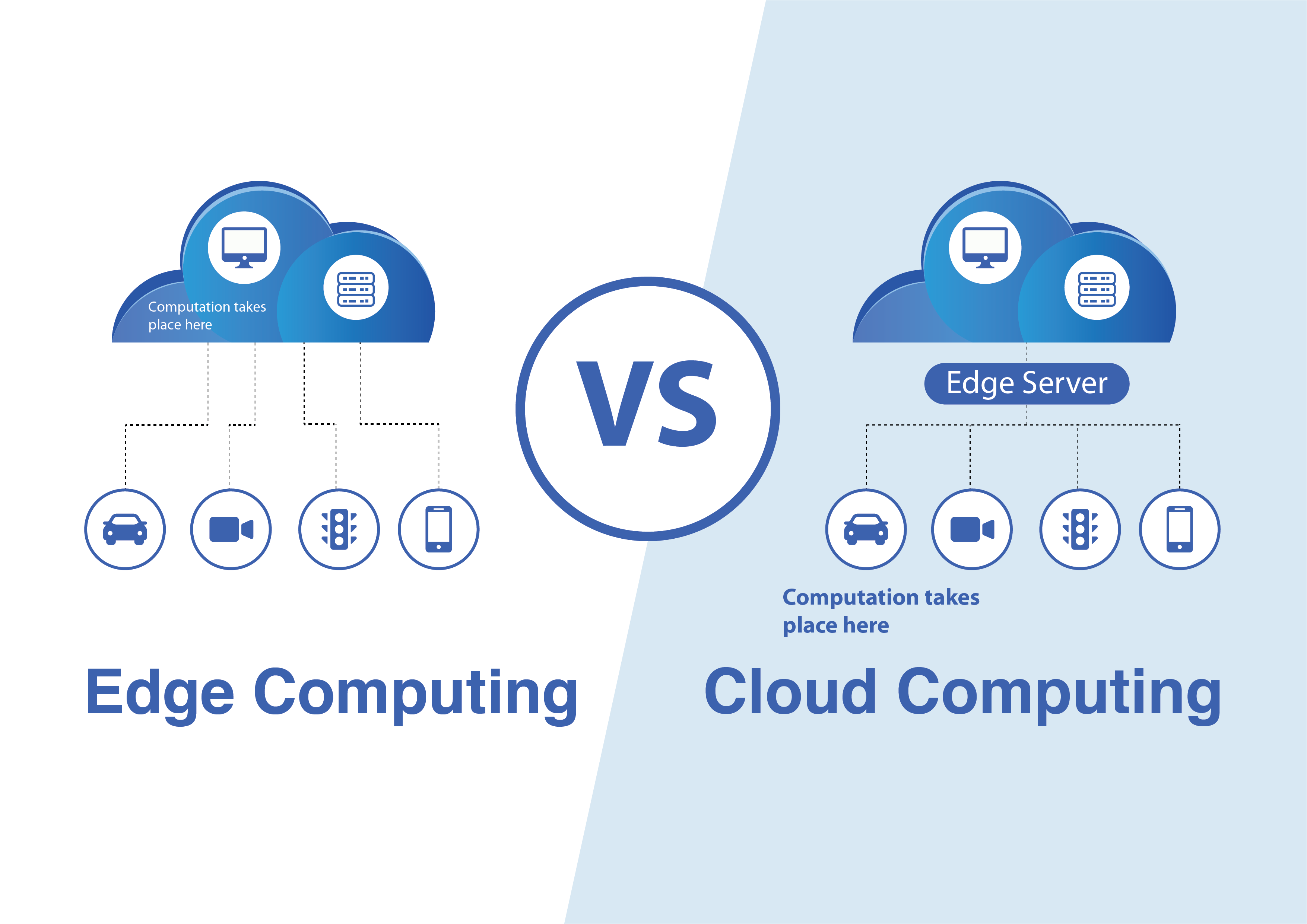
What we do
We consistently offer solutions designed to address the growing demand for edge computing, driven by factors such as reduced latency, enhanced bandwidth, privacy considerations, and increased autonomy. As an Edge computing provider, we are particularly focused on meeting the need for real-time data in applications such as augmented and virtual reality (AR and VR).
Furthermore, we provide tailored solutions to accommodate the rising bandwidth requirements stemming from the widespread adoption of IoT devices, thereby improving bandwidth utilization and availability. Additionally, we develop solutions for scenarios in network environments where sensors and actuators are expected to operate autonomously, even in the absence of a connection to the cloud. For software demanding high performance and intolerant of additional latency or for applications confined to localized service areas, edge computing offers significant advantages that traditional cloud services lack.
With the right tools in place, such as a consistent CI/CD pipeline, migrating services to the edge can resemble deployment elsewhere. The primary consideration lies in the architecture, ensuring that only appropriate code and services are moved to edge Points of Presence (POPs). Less resource-intensive services can often remain in the cloud, while edge POPs handle the resource-intensive tasks while communicating with other cloud or on-premises resources.
A well-executed edge deployment remains imperceptible to end users. When done correctly, the edge can be a minor detail for the organization and DevOps teams responsible for the deployment. As networks expand and software interconnectivity grows, the number of available edge POPs is likely to increase. Relying on edge services will become a more common deployment strategy.
We consider the edge as a natural extension of the cloud.